Understanding Sports Broadcasting Basics
What is Sports Broadcasting?
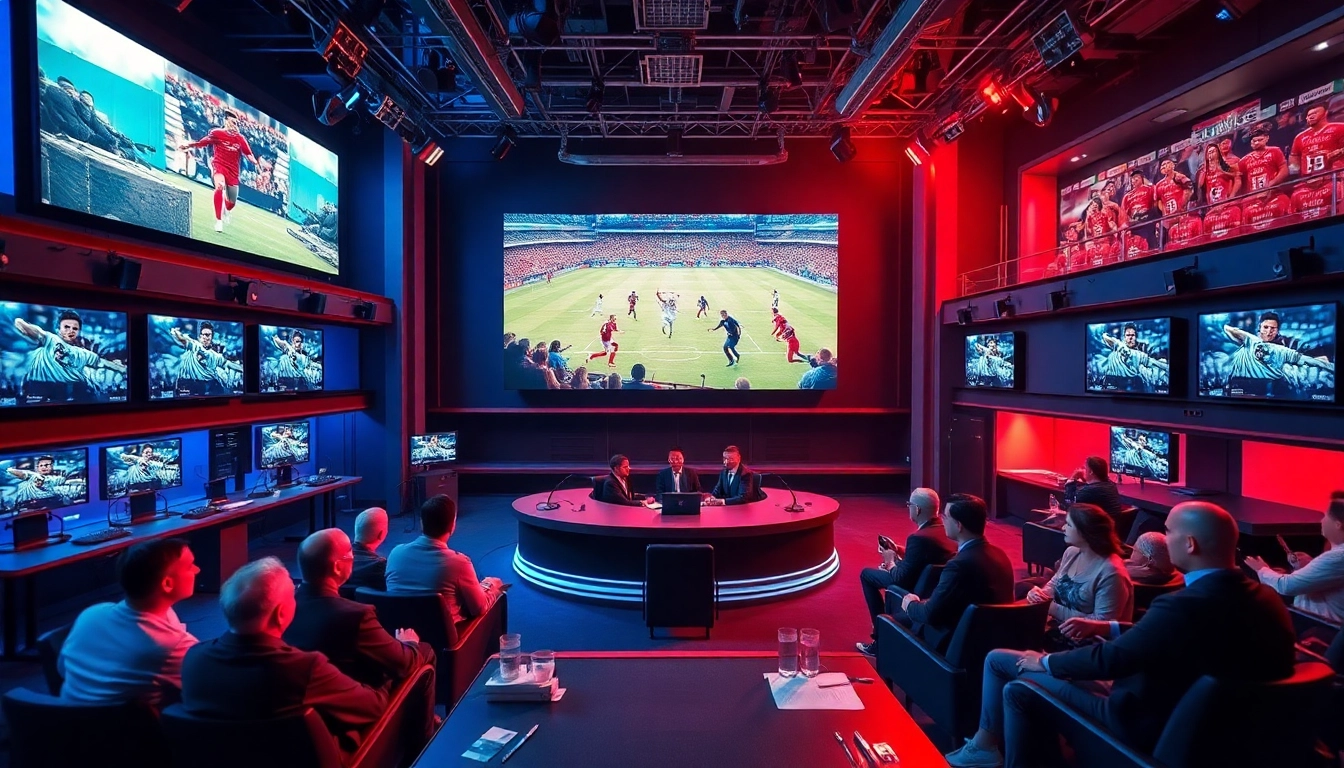
Sports broadcasting refers to the transmission of live and recorded sports events to an audience through various media channels. This includes television, radio, and digital platforms, enabling fans to experience sporting events irrespective of their location. The essence of sports broadcasting lies in bringing excitement, commentary, and analysis directly to viewers or listeners. A comprehensive understanding of sports broadcasting includes the technology used, the types of media, and the audience engagement strategies employed. A focus on Sports Broadcasting reveals insights into this dynamic field.
The Evolution of Sports Broadcasting
The landscape of sports broadcasting has undergone significant transformation since its inception. The early days saw live games being relayed through radio, the technology of the 1920s paving the way for a new form of televised sports in the 1930s. Initially, coverage was limited to select events and local broadcasts. However, with the introduction of satellite transmission in the 1980s, the potential reach expanded dramatically. Today, sports broadcasting features sophisticated analytics and multi-platform distribution, from traditional TV networks to mobile streaming applications. As technology continues to evolve, the methods and scope of sports broadcasting persistently adapt to enhance viewer experiences.
Key Components of Sports Broadcasting
Sports broadcasting comprises several key components that work in harmony. These include:
- Production: The behind-the-scenes efforts that encompass filming, directing, and editing sports events.
- Commentary: Engaging narratives provided by announcers that enhance the viewers’ understanding of the game.
- Graphics: Visual aids and on-screen data that inform fans of statistics and player performances in real-time.
- Advertising: Vital for financial sustainability, ads featured during broadcasts help to fund the production costs.
- Distribution: Various channels such as cable, satellite, and streaming services that deliver content to audiences.
Types of Sports Broadcasting Media
Television Broadcasting Explained
Television remains one of the most prominent mediums for sports broadcasting. Major networks invest heavily in acquiring broadcasting rights, allowing them to showcase live events to millions simultaneously. The integration of high-definition (HD) and ultra-high-definition (UHD) technology has revolutionized viewing experiences, providing sharper images and enhanced detail. Moreover, the rise of cable sports networks has created a diverse range of programming, catering to various sports and audiences.
Radio Sports Broadcasting
Despite the technological advancements in television and digital media, radio sports broadcasting has maintained a dedicated audience. Radio provides a unique auditory experience, allowing fans to immerse themselves in the excitement of live commentary. Many local broadcasters focus on specific teams or leagues, fostering a loyal listener base. The immediacy of radio broadcasts, combined with an engaging narrative and analysis, creates an intimate way for fans to follow their favorite sports.
Digital Platforms for Sports Broadcasting
With the influx of internet users, digital platforms have become game-changers in the field of sports broadcasting. Streaming services have enabled fans to watch games on various devices, offering on-demand access to past events and unique features such as multi-angle viewing. Social media platforms also play an essential role by facilitating live updates, highlights, and audience interaction. Mobile apps have further democratized sports content, allowing fans to engage with their teams anytime and anywhere.
Innovations in Sports Broadcasting
The Role of Technology in Sports Broadcasting
Technology is at the forefront of innovations in sports broadcasting. Advanced camera systems, like 4K and 8K resolution, provide breathtaking visuals that enhance the viewer’s experience. Additionally, artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly used for analytics and insights into player performance, leading to more informed commentary and discussion. The integration of machine learning algorithms helps broadcasters optimize live feeds and tailor content to viewer preferences, revolutionizing the entire landscape of sports media.
Live Streaming and Its Impact
Live streaming has emerged as a powerful tool in sports broadcasting, enabling real-time viewer interactions. Platforms such as Twitch and YouTube Live allow fans to watch events as they unfold, and engage with commentary from other viewers. This interactive aspect not only increases viewer engagement but also fosters community around specific sports or teams. Furthermore, live streaming has proven essential for major events like championships and tournaments, making them accessible to global audiences.
Augmented Reality in Sports Broadcasting
Augmented reality (AR) is set to shape the future of sports broadcasting by blending virtual elements into live broadcasts. This technology provides visual enhancements like player statistics overlaid during games, or strategic insights delivered in real-time. Furthermore, AR allows fans to explore immersive highlights and replays, creating a more engaged and entertained audience. As AR continues to develop, its integration into sports broadcasting will alter the way fans interact with content significantly.
Effective Strategies for Engaging Viewers
Creating Compelling Content
Compelling content is the cornerstone of effective sports broadcasting. Quality production values, including crisp visuals and clear sound, create an enjoyable viewing experience. Adding expert analysis and storytelling elements can further draw in audiences, allowing them to connect more deeply with the events taking place. Emphasizing human interest stories related to athletes and teams can resonate strongly, creating emotional bonds with the audience.
Utilizing Social Media for Sports Broadcasting
Social media platforms are invaluable assets for sports broadcasters to engage with fans beyond traditional broadcasts. Utilizing platforms like Twitter, Instagram, and TikTok, broadcasters can share highlights, gather fan interactions, and spark discussions. Creating a unique, compelling online presence helps broadcasters capture the attention of younger audiences who are increasingly consuming sports content online. Moreover, real-time updates on social media allows fans to remain informed and connected with ongoing events.
Building a Community Around Sports Broadcasting
A strong community enhances viewer loyalty and participation in sports broadcasting. Establishing online forums or fan clubs can create spaces for passionate discussions and shared experiences. Engaging with the audience through Q&A sessions, polls, and live chats fosters deeper relationships. Additionally, featuring fan-generated content, such as stories and photos, encourages community involvement and strengthens the broadcaster’s connection with the audience.
Measuring Success in Sports Broadcasting
Key Performance Indicators
Effective measurement of success in sports broadcasting relies on identifying relevant key performance indicators (KPIs). Metrics such as viewership ratings, audience demographics, and engagement levels are commonly evaluated. Beyond traditional metrics, broadcasters need to leverage analytics to gain insights into viewer preferences, which can guide future programming decisions and marketing strategies. Analyzing these KPIs allows organizations to strategically enhance their broadcasting effectiveness and audience satisfaction.
Audience Engagement Metrics
Measuring audience engagement provides broadcasters with valuable insights into viewer interactions with content. Metrics such as social media shares, comments, and likes reflect audience interest and acceptance of the broadcast. Viewer retention rates reveal how well content holds audience attention. Surveys and feedback can offer qualitative data on audience preferences. Combining quantitative metrics with qualitative insights creates a comprehensive understanding of audience engagement, paving the way for more tailored content.
Adjusting Strategies Based on Analytics
Utilizing analytics to adapt strategies is vital for effective sports broadcasting. Review of past broadcasts and current viewer behavior can identify trends and opportunities for improvement. For example, if data suggests a drop in viewership during specific segments, broadcasters can analyze the causes and implement changes in real-time. Continuous adjustment ensures content remains fresh and engaging, ultimately optimizing audience retention and satisfaction.
FAQs About Sports Broadcasting
What is the primary goal of sports broadcasting?
The primary goal of sports broadcasting is to deliver live or recorded sports events to a wide audience while providing engaging commentary and analysis to enhance the viewer’s understanding and enjoyment.
How has technology impacted sports broadcasting?
Technology has greatly enhanced sports broadcasting by introducing high-definition visuals, analytics, and live streaming, making sports more accessible and engaging for audiences globally.
Why is audience engagement important in sports broadcasting?
Audience engagement is crucial because it fosters loyalty, influences viewership rates, and enhances the overall experience for fans, ultimately leading to increased revenue for broadcasters.
What metrics are used to measure success in sports broadcasting?
Success in sports broadcasting is measured through viewership ratings, audience demographics, engagement levels, and retention rates, among other key performance indicators.
What role does social media play in sports broadcasting?
Social media amplifies the reach of sports broadcasts by providing real-time updates, fan interactions, and creating a community around events, thus enhancing viewer engagement.